Static Keyword in Java:
The static keyword in Java is used to create class-level variables and methods. These members are shared across all instances of the class, meaning they are class-wide and not tied to individual object instances.
Static Variables (Fields)
Static variables, also referred to as class variables or fields, are shared among all instances of a class. These variables are initialized only once and are common to every object of that class.
Static Methods
Static methods can be called without creating an instance of the class. These methods can only access other static members (variables and methods) within the class.
Example code for Static and Local Variables in Java:
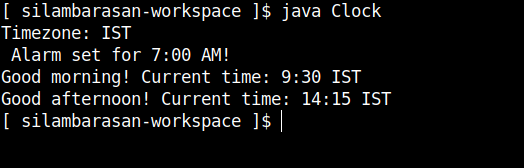
public class Clock {// Staticstatic String timezone = "IST";static void setAlarm() {System.out.println(" Alarm set for 7:00 AM!");}// Non-static - decleartionint hours;int minutes;void displayTime() {String greeting; // Local variableif (hours < 12) greeting = "Good morning!";else if (hours < 18) greeting = "Good afternoon!";else greeting = "Good evening!";System.out.println(greeting + " Current time: " + hours + ":" + minutes + " " + timezone);}public static void main(String[] args) {// Static accessSystem.out.println("Timezone: " + Clock.timezone);Clock.setAlarm();// Time objectsClock t1 = new Clock();t1.hours = 9;t1.minutes = 30;// Non-static callst1.displayTime();}}public class Clock { // Static static String timezone = "IST"; static void setAlarm() { System.out.println(" Alarm set for 7:00 AM!"); } // Non-static - decleartion int hours; int minutes; void displayTime() { String greeting; // Local variable if (hours < 12) greeting = "Good morning!"; else if (hours < 18) greeting = "Good afternoon!"; else greeting = "Good evening!"; System.out.println(greeting + " Current time: " + hours + ":" + minutes + " " + timezone); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Static access System.out.println("Timezone: " + Clock.timezone); Clock.setAlarm(); // Time objects Clock t1 = new Clock(); t1.hours = 9; t1.minutes = 30; // Non-static calls t1.displayTime(); } }public class Clock { // Static static String timezone = "IST"; static void setAlarm() { System.out.println(" Alarm set for 7:00 AM!"); } // Non-static - decleartion int hours; int minutes; void displayTime() { String greeting; // Local variable if (hours < 12) greeting = "Good morning!"; else if (hours < 18) greeting = "Good afternoon!"; else greeting = "Good evening!"; System.out.println(greeting + " Current time: " + hours + ":" + minutes + " " + timezone); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Static access System.out.println("Timezone: " + Clock.timezone); Clock.setAlarm(); // Time objects Clock t1 = new Clock(); t1.hours = 9; t1.minutes = 30; // Non-static calls t1.displayTime(); } }
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
Code Output:
Note: The document formatting and structure were assisted by ChatGPT.
————————— End of the Blog ——————————-
原文链接:Day-15: Static vs Non-Static Methods, Global vs Local Variables in Java









暂无评论内容