Java Data Types
Primitive Data Types
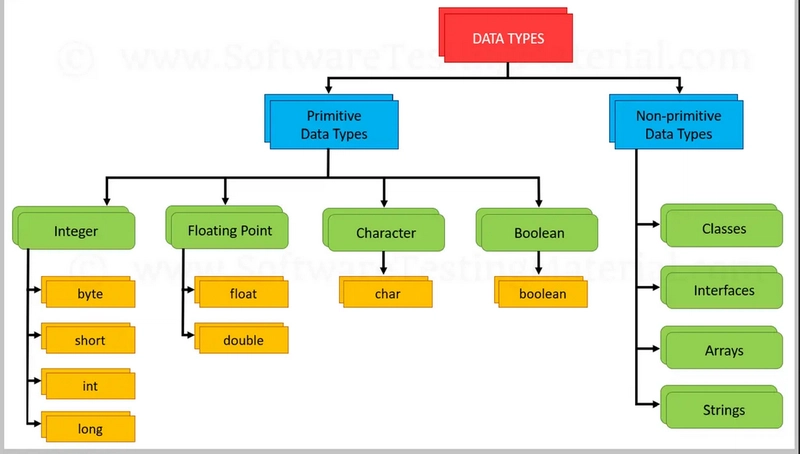
Primitive data types are the most basic data types available in Java. There are eight primitive data types, each serving a specific purpose:
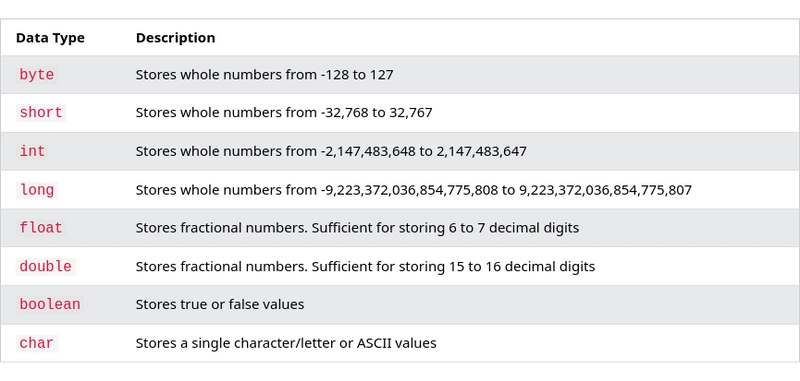
byte:
Size: 8-bit
Range: -128 to 127
Usage: Memory-efficient storage in large arrays.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
byte b = 100;
Powered By
short:
Size: 16-bit
Range: -32,768 to 32,767
Usage: Suitable for saving memory in large arrays.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
short s = 10000;
Powered By
int:
Size: 32-bit
Range: -231 to 231-1
Usage: Default choice for integer values.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
int i = 100000;
Powered By
long:
Size: 64-bit
Range: -263 to 263-1
Usage: For large integer values.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
long l = 100000L;
Powered By
float:
Size: 32-bit
Usage: For fractional numbers, with single precision.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
float f = 234.5f;
Powered By
double:
Size: 64-bit
Usage: For fractional numbers, with double precision.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
double d = 123.4;
Powered By
boolean:
Values: true or false
Usage: For simple flags and conditions.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
boolean flag = true;
Powered By
char:
Size: 16-bit
Range: 0 to 65,535 (Unicode characters)
Usage: For storing characters.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
char c = ‘A’;
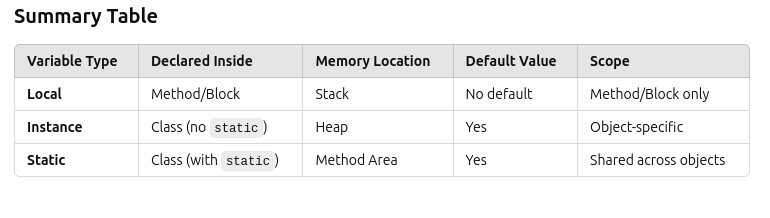
Types of Variables in Java
In Java, variables are classified into three main types:
-
Local Variables
Declared inside a method, constructor, or block.
Scope is limited to the block where they are declared.
Must be initialized before use.
Example:
public class LocalVariableExample {
public void display() {
int num = 10; // Local variable
System.out.println(“Local Variable: ” + num);
}
}
-
Instance Variables
Declared inside a class but outside any method.
Belongs to an instance of the class (each object gets its own copy).
Initialized with default values if not explicitly assigned.
Example:
public class InstanceVariableExample {
int age = 25; // Instance variable
public void show() {
System.out.println("Instance Variable: " + age);
}
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
}
Default values for instance variables:
int → 0
double → 0.0
boolean → false
String (or any object) → null
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
-
Static Variables (Class Variables)
Declared using the static keyword inside a class but outside methods.
Shared among all objects of the class (common memory).
Initialized once at class loading.
Example:
public class StaticVariableExample {
static String company = “Tech Corp”; // Static variable
public void show() {
System.out.println("Static Variable: " + company);
}
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
}
Complete example:








暂无评论内容