Introduction to Java: A Beginner’s Guide
Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, known for its platform independence, security, and versatility.
What is Java?
Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle Corporation) in 1995. It is designed to be simple, secure, and platform-independent, making it a preferred language for software development across various domains.
Key Features of Java
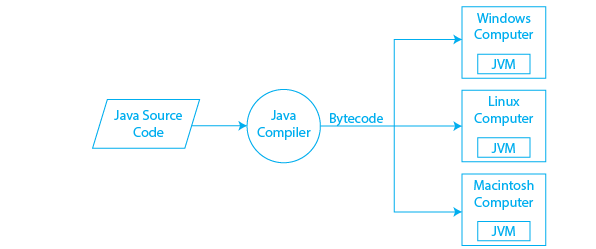
Platform Independence: Java’s “Write Once, Run Anywhere” (WORA) principle allows programs to run on any operating system with a JVM.
Object-Oriented: Java uses classes and objects to structure programs efficiently.
Automatic Memory Management: Java’s Garbage Collection automatically handles memory allocation and deallocation.
Security: Java provides built-in security features like bytecode verification and sandboxed execution.
Multithreading: Java supports concurrent execution, improving program efficiency.
Rich Libraries: Java offers pre-built APIs for tasks like networking, database access, and file handling.
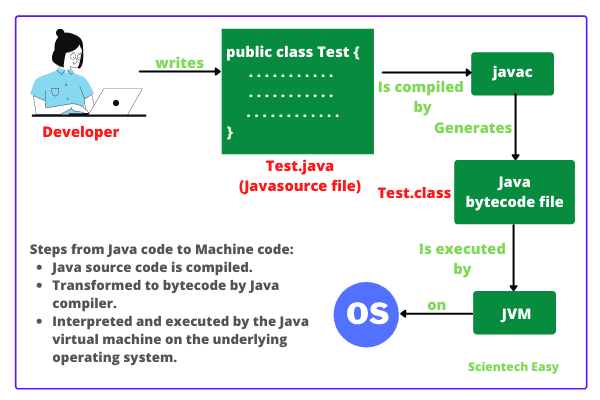
How Java Works
Java programs follow these steps:
Compilation: Java code (.java file) is compiled into bytecode (.class file) using javac.
Execution: The JVM interprets and runs the bytecode on any compatible platform.
Basic Java Program
public class HelloJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello, Java!”);
}
}
Applications of Java
Java is used in many fields, including:
-Web Development (Spring, JSP, Servlets)
-Mobile Development (Android apps)
-Enterprise Software (Banking, E-commerce)
-Game Development (LibGDX, jMonkeyEngine)
-Cloud Computing & Big Data (Hadoop, Apache Spark)
Key Features of a Java Compiler:
Syntax Checking: Ensures the code follows Java’s rules.Type Checking: Detects incorrect data type usage.Bytecode Generation: Converts code into an intermediate format for the JVM.Optimization: Improves performance by optimizing the bytecode.Syntax Checking: Ensures the code follows Java’s rules. Type Checking: Detects incorrect data type usage. Bytecode Generation: Converts code into an intermediate format for the JVM. Optimization: Improves performance by optimizing the bytecode.Syntax Checking: Ensures the code follows Java’s rules. Type Checking: Detects incorrect data type usage. Bytecode Generation: Converts code into an intermediate format for the JVM. Optimization: Improves performance by optimizing the bytecode.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode
Common Java Compilers:
javac (Java Compiler) – Comes with the JDK.Eclipse Compiler for Java (ECJ) – Used in the Eclipse IDE.JIT Compiler (Just-In-Time Compiler) – Part of the JVM, converts bytecode into native machine code at runtime.javac (Java Compiler) – Comes with the JDK. Eclipse Compiler for Java (ECJ) – Used in the Eclipse IDE. JIT Compiler (Just-In-Time Compiler) – Part of the JVM, converts bytecode into native machine code at runtime.javac (Java Compiler) – Comes with the JDK. Eclipse Compiler for Java (ECJ) – Used in the Eclipse IDE. JIT Compiler (Just-In-Time Compiler) – Part of the JVM, converts bytecode into native machine code at runtime.
Enter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode









暂无评论内容